

Two common frame types are these: Value Description 0x0800 IPv4 Protocol 0x0806Ĭontains the encapsulated upper-level protocol. There are numerous upper-layer protocols supported by Ethernet II. The source address is always unicast.įor Ethernet II frames, this field contains a hexadecimal value that is used to indicate the type of upper-layer protocol in the data field. The destination address may be a broadcast, which contains all ones, or a unicast. The first six hex numbers indicate the manufacturer of the network interface card (NIC), the last six hex numbers are the serial number of the NIC. Each address is 48 bits long, or 6 octets, expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits, 09,A-F. This field contains synchronizing bits, processed by the NIC hardware. The following table takes the first frame in the Wireshark capture and displays the data in the Ethernet II header fields. Step 4: Examine the Ethernet II header contents of an ARP request. Lab – Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames session begins with an ARP query for the MAC address of the gateway router, followed by four ping requests and replies. A filter has been applied to Wireshark to view the ARP and ICMP protocols only.
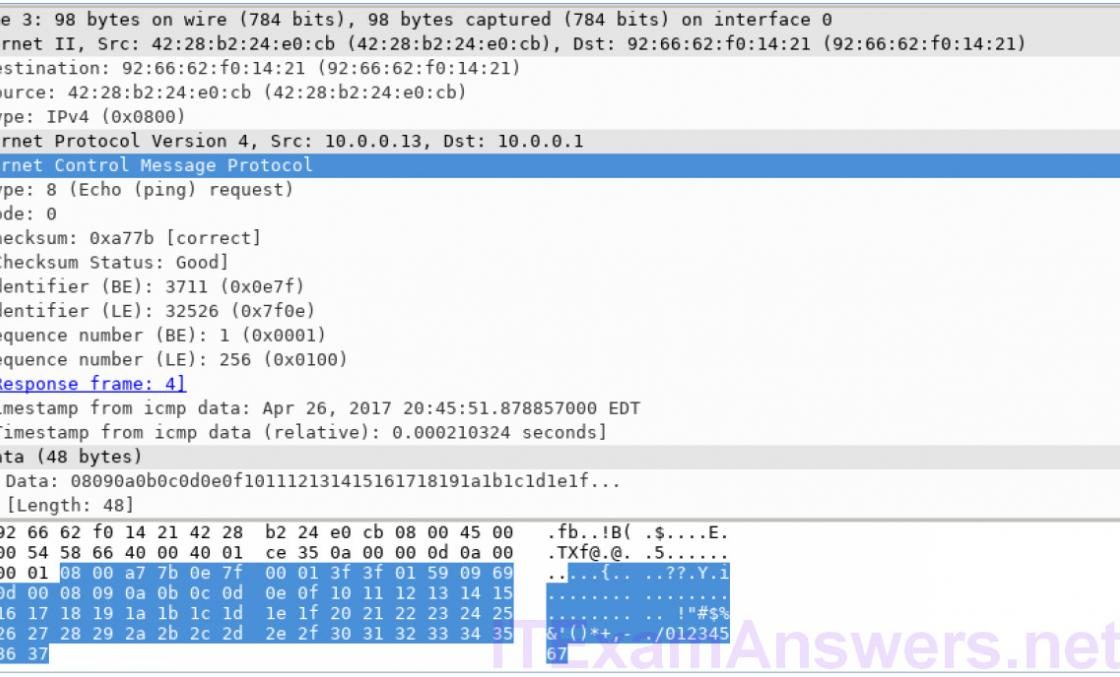
The Wireshark capture below shows the packets generated by a ping being issued from a PC host to its default gateway. Step 3: Examine Ethernet frames in a Wireshark capture. This PC host IP address is 192.168.1.147 and the default gateway has an IP address of 192.168.1.1. Step 2: Examine the network configuration of the PC. Lab – Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames Step 1: Review the Ethernet II header field descriptions and lengths. A Wireshark capture will be used to examine the contents in those fields. Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame In Part 1, you will examine the header fields and content in an Ethernet II frame. In Part 2, you will use Wireshark to capture and analyze Ethernet II frame header fields for local and remote traffic.ġ PC (Windows 7, 8, or 10 with internet access with Wireshark installed) In the first part of this lab, you will review the fields contained in an Ethernet II frame. When learning about Layer 2 concepts, it is helpful to analyze frame header information. For example, if the upper layer protocols are TCP and IP and the media access is Ethernet, then the Layer 2 frame encapsulation will be Ethernet II. The frame composition is dependent on the media access type.


Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Framesīackground / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with each other, data flows down the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) layers and is encapsulated into a Layer 2 frame. Lab – Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames Topology


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
